Written Expression
Section outline
-

Dr. Yasser BEN MOUSSA, Assistant lecturer
- Faculty of Letters and Foreign Languages, at Mohamed Khieder University of Biskra
- Department of English Language and Literature
- Contact: yasser.benmoussa@univ-biskra.dz
Course Details
- Written Expression, also refers to ' WE'
- Teaching Time: 2hours per week
- Setting: Monday from 08:00am to 9:00am at Room 15.
- Tuesday from 9.40 am to 11.10 at room 25
- For First year LMD
- Group 15
- Coefficient: 2
- Credit: 2
- Unit: Fundamental
Availability
- Office: Staff-room 2. Tuesday, from 10am- 13:00, at the Department of English.
- Forum Discussion: If you have questions related to the course, or the assignment, you can post them in the forum space. I will be able to answer you back during 48hours.
- Email: I also answer emails, in case I am in an annual leave, you will receive an automatic reply that informs you about my non-availability. In urgent situations, I reply through emails, however, the way that I prefer we contact each other is through the forum.
-

Learning Objectives: by the completion of this semester, students will be able to
Demonstrate the ability to comprehend and express ideas in written form in the language of study, producing coherent and well-structured texts.
Develop textual, metatextual, and linguistic knowledge by analyzing and engaging with a variety of text types, and apply this knowledge to create original written work.
Acquire and enhance reading and writing skills, including the use of effective strategies for comprehension, analysis, and composition.
Distinguish between literal and inferential meanings in texts, and apply this understanding to interpret and analyze written material effectively.
- LO1: what is a sentence
- LO2: Identify the four types of sentences based on function (declarative, interrogative, imperative, exclamatory) and provide examples of each.
- LO3: Point out the key differences between simple, compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences based on their structure and clause types.
- LO4: Examine how punctuation marks (periods, question marks, exclamation marks) are used to distinguish between sentence types based on their function.
-
Objectives designed for the pre-requisites are interrelated to what students know (de savoir ce que savent), and what students need to develop to be able to apply writing skills.
Recognition of nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, and articles.
Understanding subjects (who/what the sentence is about) and verbs (action/state of being).
The concept of a complete thought (a sentence must express a full idea).
-
Activity One: Highlight the subject and the verb in each sentence.
1. The dog barks loudly.
2. Maria reads a book.
3. Birds fly south in winter.
4. The teacher explains the lesson.
5. We eat dinner at 7 PM. Highlight.
Activity Two: Identify the bolded word's part of speech (noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, article).
The quick fox jumps.
A
Adjective
B
adverb
Activity Three: Identify the bolded word's part of speech (noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction, article).
. She sings beautifully.
A
Verb
B
Preposition
Activity Four: Identify if the statement is a complete sentence or it's a fragment.
On the tall mountain.
A
Compete sentence
B
Fragment
-
-
Opened: Wednesday, 13 August 2025, 9:46 AMClosed: Monday, 18 August 2025, 9:46 AM
-
-
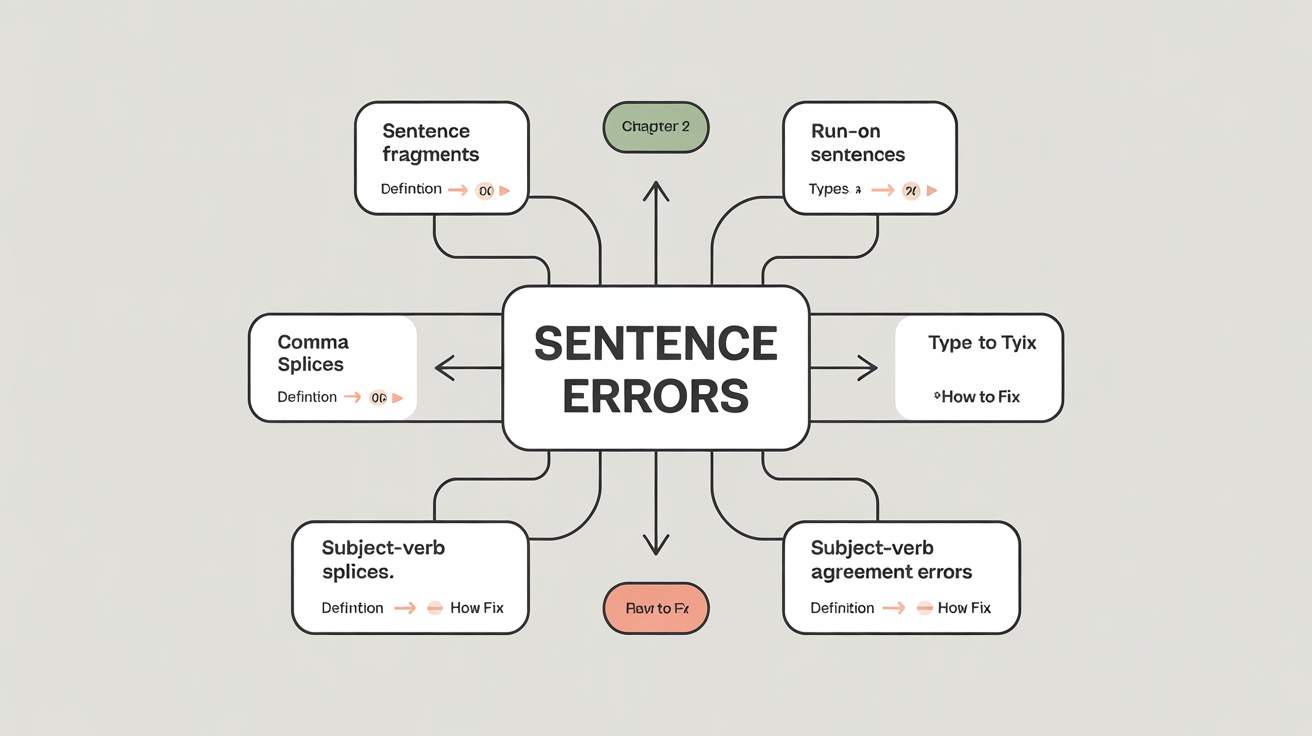 Sentence errors are common grammatical mistakes that hinder clarity and correctness in writing. They include issues like fragments (incomplete sentences), run-ons (multiple independent clauses improperly joined), comma splices (commas incorrectly connecting independent clauses), and subject-verb agreement errors (when the verb form doesn't match its subject in number). Identifying and correcting these errors is crucial for effective writing.
Sentence errors are common grammatical mistakes that hinder clarity and correctness in writing. They include issues like fragments (incomplete sentences), run-ons (multiple independent clauses improperly joined), comma splices (commas incorrectly connecting independent clauses), and subject-verb agreement errors (when the verb form doesn't match its subject in number). Identifying and correcting these errors is crucial for effective writing. -
Read each group of words below. Identify whether it is a sentence fragment (F) or a complete sentence (S). If it is a fragment, rewrite it as a complete sentence.
Part 1: Identify Fragments
The sun set behind the mountains, casting a warm glow over the valley.
2. _ __ Because I was late to the meeting.
3. __ _ Running through the park in the morning
4. _ __ She enjoys reading novels on weekends.
5. When the sun sets over the horizon.
6. __ The students studied for their exams.
7. __ _ Although it was raining heavily.
8. ___ My brother loves to play soccer with his friends.
Quiz: Identify sentence errors in the below paragraph.
When I woke up this morning. I realized I was late for school, I rushed to get ready, I forgot to eat breakfast. Running out the door with my backpack. Because I didn't want to miss the bus. The bus was already leaving, I had to run after it, the driver didn't see me. Although I was out of breath. I finally caught up to the bus, the driver let me on. Sitting in my seat, feeling relieved. My friend asked me why I was so late, I told her about my morning, she laughed. After I got to school, everything was fine.
-
Activity One Read each group of words below. Identify fragment, rewrite it as a complete sentence.
Part 1: Identify Fragments
The sun set behind the mountains, casting a warm glow over the valley.
2. _CS__ Because I was late to the meeting.
3. __F_ Running through the park in the morning.
4. _F__ She enjoys reading novels on weekends.
5. __CS_ When the sun sets over the horizon.
6. __CS_ The students studied for their exams.
7. __F_ Although it was raining heavily.
8. CS___ My brother loves to play soccer with his friends.
Corrected paragraph
When I woke up this morning, I realized I was late for school. I rushed to get ready and forgot to eat breakfast. I ran out the door with my backpack because I didn't want to miss the bus. The bus was already leaving, so I had to run after it, but the driver didn't see me. Although I was out of breath, I finally caught up to the bus, and the driver let me on. I sat in my seat, feeling relieved. My friend asked me why I was so late, and I told her about my morning. She laughed. After I got to school, everything was fine.
-

-
Opened: Thursday, 14 August 2025, 11:14 AMClosed: Thursday, 14 August 2025, 11:14 AM
-
-
Khan, S. (2024). Kind of sentences: Assertive, interrogative, imperative, optative, exclamatory sentences; English grammar. Sakha Global Books, Inc.
Coker, D. L., & Ritchey, K. D. (2015). Teaching beginning writers. Guilford Publications.
Bartle, P. (2006). Grammar and composition: A comprehensive guide. Academic Press.
Vito, G. (2006). Mastering punctuation and grammar: A practical guide. Language Press.
-
-
Opened: Friday, 22 August 2025, 12:00 AMDue: Friday, 29 August 2025, 12:00 AM
-
Opened: Monday, 25 August 2025, 12:00 AMDue: Monday, 1 September 2025, 12:00 AM


