Genetics
Résumé de section
-
Specific objectifs of this chapter:
- Grasp the molecular composition and physical characteristics of DNA and its role in genetic informationstorage.
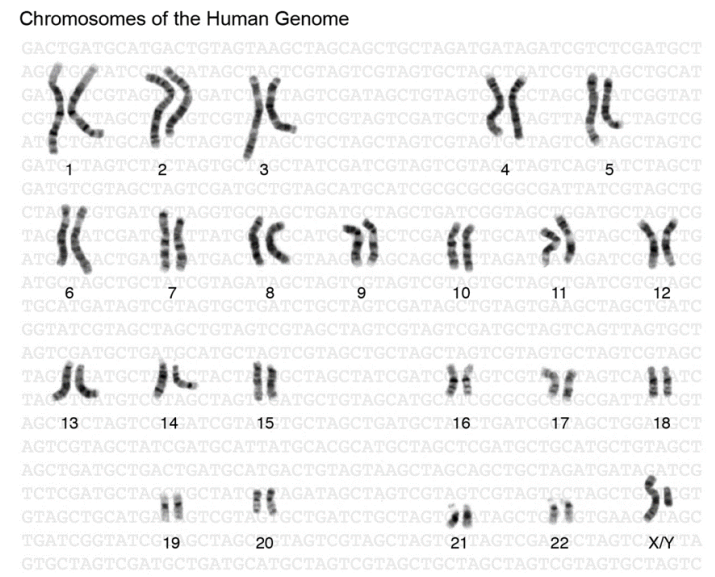
- Understand chromosome organization and formation, as well as the processes of cell
division and their role in genetic mixing. - Describe the role of meiosis in gamete formation and its connection to inheritance.
- Learn about chromosomal mutations, identifying their types, causes, and classifying
them in studied examples.
-
This video explains the process of Mitosis with 3D animations for more understanding.
-
This video explains with 3D animations the process of meiosis and its results.
-