incoterms
Section outline
-
-
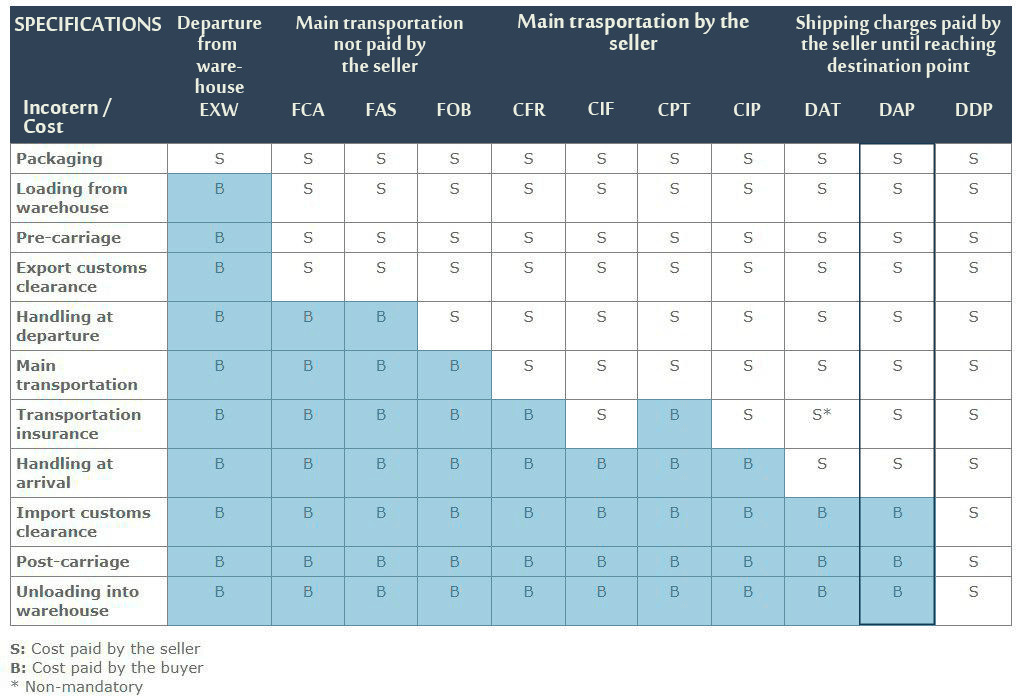
Incoterms, short for **International Commercial Terms**, are a set of globally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Established by the **International Chamber of Commerce (ICC)**, these terms clarify various aspects of shipping and delivery, including:
- **Transfer of Risk**: When does the responsibility for the goods shift from the seller to the buyer?
- **Cost Allocation**: Who is responsible for transportation costs, insurance, and other expenses?
- **Delivery Points**: Where must the goods be delivered?Incoterms are not legally binding unless included in a sales contract, but they provide a standardized framework that helps prevent misunderstandings in international transactions. The latest version, **Incoterms 2020**, includes 11 terms that are applicable to different modes of transport, with some terms specifically designed for maritime transport.
### Key Incoterms (2020)
1. **EXW (Ex Works)**: The seller makes the goods available at their premises; the buyer assumes all risks and costs from that point.
2. **FCA (Free Carrier)**: The seller delivers goods to a carrier chosen by the buyer at a specified location.
3. **CPT (Carriage Paid To)**: The seller pays for transportation to a specified destination, but risk transfers to the buyer upon delivery to the carrier.
4. **CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To)**: Similar to CPT, but the seller also provides insurance.
5. **DAP (Delivered at Place)**: The seller is responsible for all costs and risks until the goods are delivered at a specified location.
6. **DPU (Delivered at Place Unloaded)**: The seller delivers and unloads the goods at a specified destination.
7. **DDP (Delivered Duty Paid)**: The seller assumes all costs and risks until the goods are delivered and cleared for import.For sea transport, additional terms include:
- **FAS (Free Alongside Ship)**
- **FOB (Free on Board)**
- **CFR (Cost and Freight)**
- **CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight)**These terms help facilitate smooth transactions by providing clarity on each party's obligations and minimizing potential disputes during shipping processes[1][2][4][6].
Citations:
[1] https://www.time-matters.com/emergency-logistics-glossary/incoterms/
[2] https://www.ups.com/us/en/supplychain/resources/glossary-term/incoterms.page
[3] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Incoterm
[4] https://www.investopedia.com/terms/i/incoterms.asp
[5] https://www.xeneta.com/blog/incoterms
[6] https://www.acerislaw.com/incoterms-in-international-trade/
[7] https://www.dhl.com/nl-en/home/global-forwarding/freight-forwarding-education-center/incoterms-explained.html
[8] https://www.lloydsbank.com/business/resource-centre/business-guides/incoterms.html -
version francaise
-
-
-
Incoterms Overview
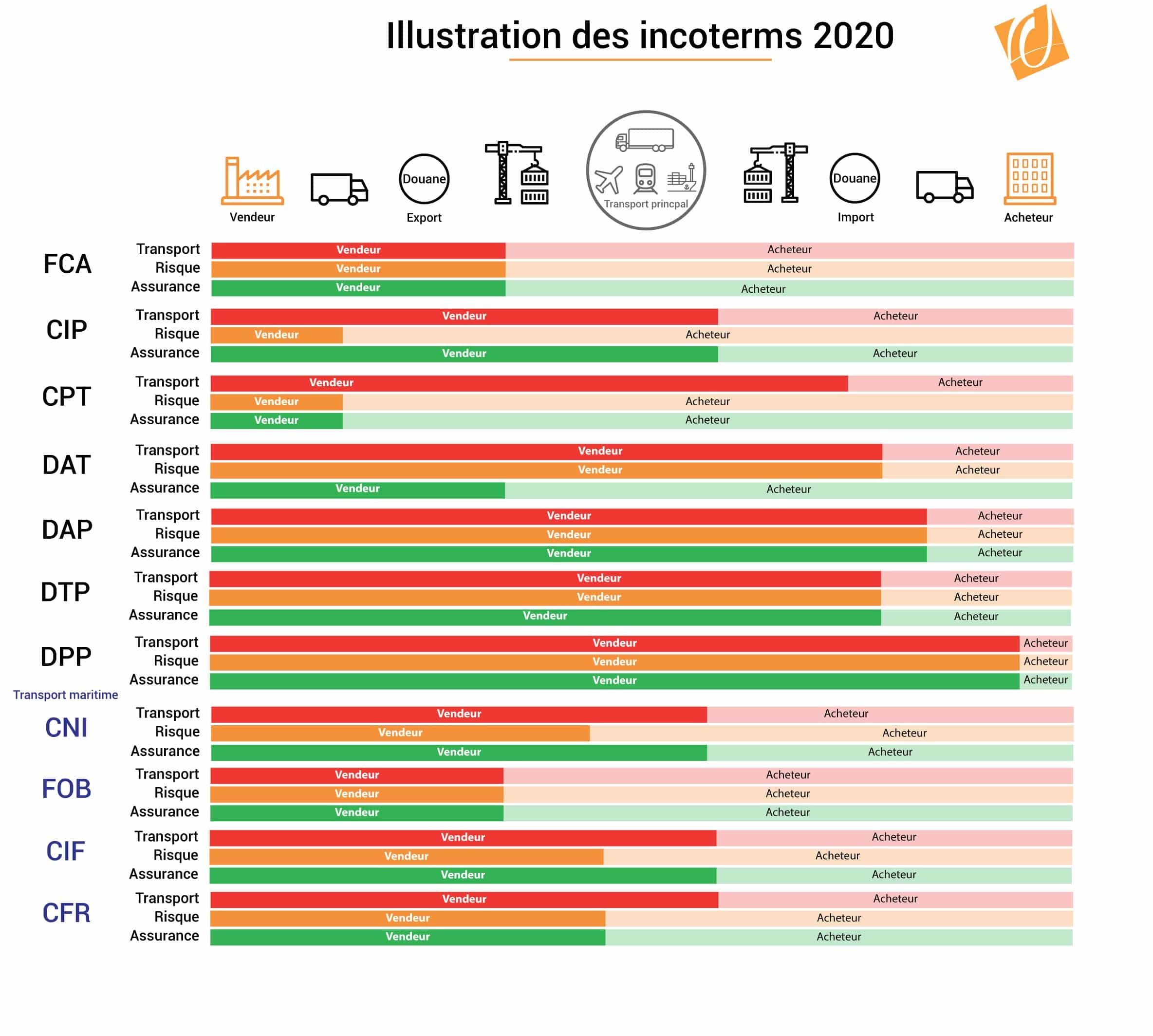
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international contracts. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, duties, and risk at various stages of the transportation process.Key Incoterms (2020)
EXW (Ex-Works)
Seller makes goods available at their premises.
Buyer assumes all risks and costs from that point.
FCA (Free Carrier)
Seller delivers goods to a carrier named by the buyer.
Risk transfers to the buyer at the point of delivery.
CPT (Carriage Paid To)
Seller pays for transport to a specified destination.
Risk transfers to the buyer once goods are handed to the carrier.
CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To)
Similar to CPT, but seller also provides insurance for the goods during transit.
DAP (Delivered at Place)
Seller delivers goods ready for unloading at the named destination.
Seller bears all risks and costs up to that point.
DPU (Delivered at Place Unloaded)
Seller delivers and unloads goods at the destination.
Seller covers all costs and risks until unloading.
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid)
Seller delivers goods cleared for import at the buyer's location.
Seller bears all costs including duties and risks.
Incoterms for Seaborne Freight Only
FAS (Free Alongside Ship)
Seller delivers goods alongside the vessel.
Risk transfers when goods are alongside.
FOB (Free on Board)
Seller delivers goods on board the vessel.
Risk transfers once goods are on board.
CFR (Cost and Freight)
Seller pays for transport to the destination port.
Risk transfers when goods are on board.
CIF (Cost, Insurance and Freight)
Seller pays for transport and insurance to the destination port.
Risk transfers when goods are on board.
Importance of Incoterms
Clarity: Reduces ambiguity in international trade agreements.
Risk Management: Clearly defines where risk transfers from seller to buyer.
Cost Allocation: Establishes who is responsible for shipping and insurance costs.
Usage of Incoterms
Include Incoterms in contracts to ensure all parties understand their responsibilities.
Refer to the latest version (Incoterms 2020) for current definitions and rules.
Understanding and correctly applying Incoterms is crucial for effective international trade and logistics management.
-
-
-
2020 updates
media in arabic
-
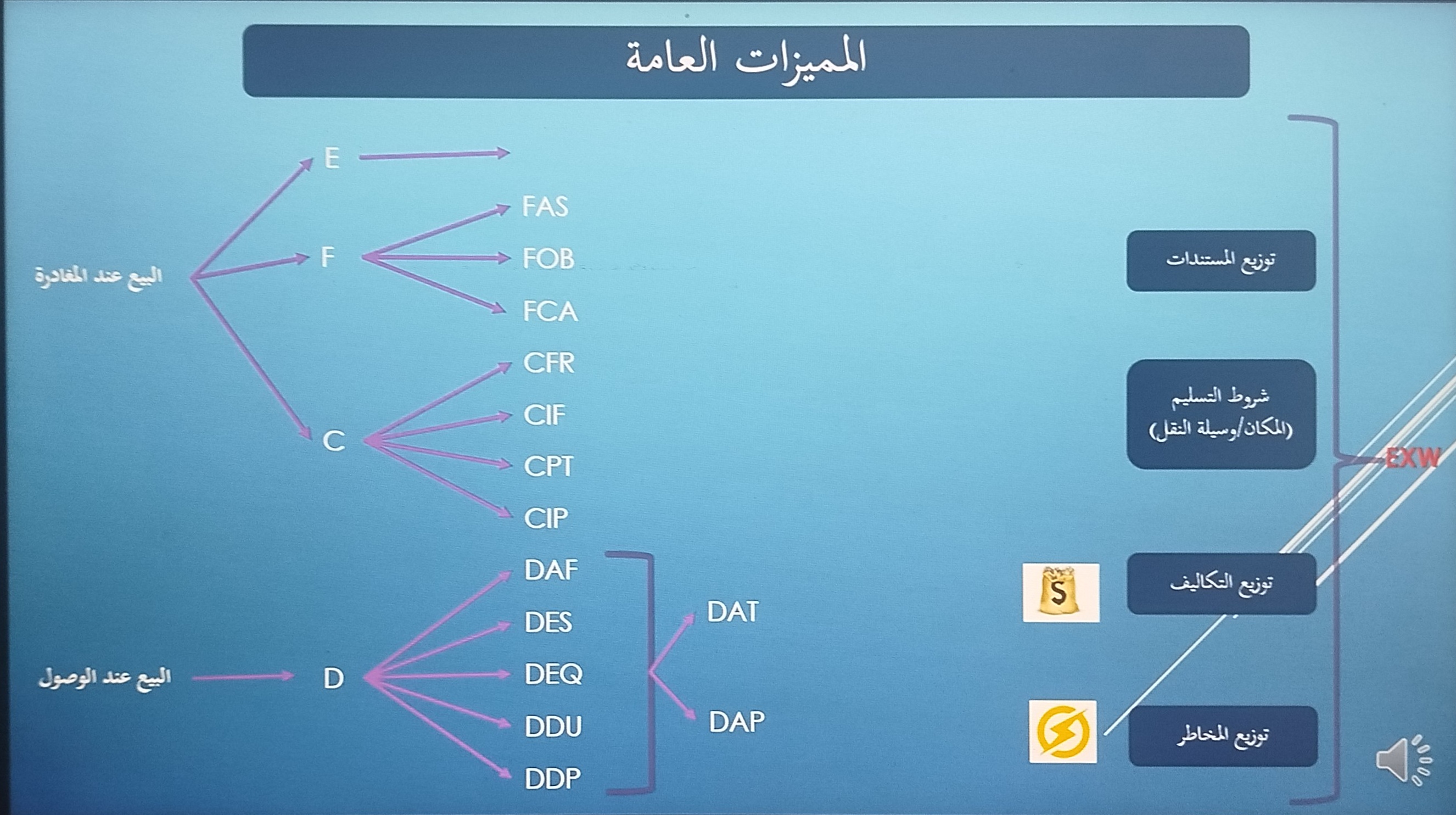
ماهي مصطلحات وقواعد التجارة الدولية
-
تحديد مسؤوليات كل هيئة ضمن الانكوترمز
-
دور البائع اكس وركس
-
free carrier
-
البائع يجهز البضاعة لوصلها لجنب الرصيف
-
من اقدم المصطلحات في النقل البحري
-
في سنة 1919 اعلن رسميا عن انشاء غرفة التجارة الدولية واختير مقرها في باريس - فرنسا ، كان لها دور مهم في وضع مجموعة من القواعد الدولية المرجعية في عدة مجالات ، لكن .. في 1936 أنشأت مصطلحات التجارة الدولية
-
-
-
various types of contracts in incoterms
أنواع مختلفة من العقود في الشروط المتفق عليها
-
-
-
Les incoterms ou termes de vente sont utilisés dans le cadre des opérations d’achat et de vente à l’international. Ils déterminent de manière précise, la répartition des coûts et des risques entre l’exportateur et l’importateur, au moment de la conclusion du contrat de vente
-