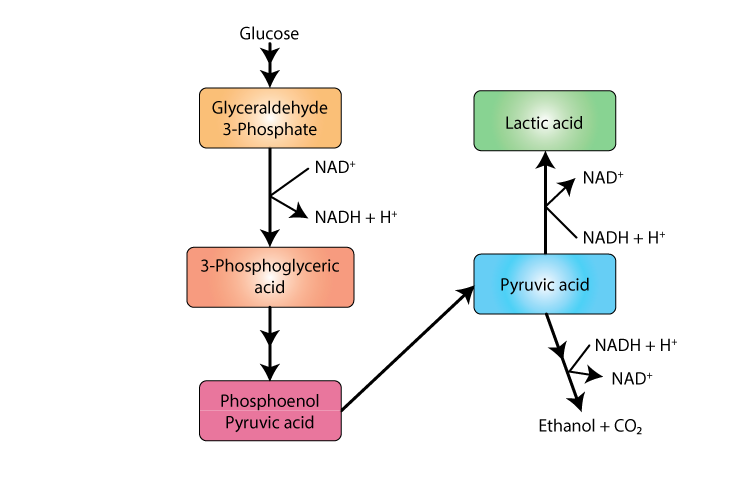
This module enables students to understand microbial metabolic pathways, identify bacteria based on biochemical reactions, and apply this knowledge in research and industry.
- Créateur de cours: manel djouama
The micobial genetics course provides a comprehensive overview of microbial genetic systems, covering the structure and organization of genetic material (chromosomes, plasmids, viral genomes), mutation and DNA repair mechanisms, genetic recombination and transposable elements, and bacterial gene transfer methods (conjugation, transformation, transduction). The course also explores restriction-modification systems, gene expression regulation in bacteria and yeast, and bacteriophage genetics including viral replication, genetic recombination, and prophage maintenance, providing students with essential knowledge for understanding microbial genetics and its biotechnology applications.
- Créateur de cours: Kenza Mohammedi

The course “Data Analysis in Biosciences” introduces students to the fundamental statistical methods used in biological research. It focuses on understanding how to collect, analyze, and interpret experimental data to draw meaningful scientific conclusions.
The course is structured around three main modules:
-
Estimation – Students learn how to estimate population parameters using sample data. This includes concepts of point estimation, interval estimation (confidence intervals), and the properties of estimators such as bias, efficiency, and consistency.
-
Hypothesis Testing – This module covers the principles and procedures for testing statistical hypotheses. It introduces null and alternative hypotheses, types of errors, significance levels, p-values, and tests for means and proportions. Applications in biological experiments are emphasized.
-
One-Way ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) – Students are introduced to the analysis of variance technique used to compare the means of more than two groups. The module explains the logic of ANOVA, assumptions of the model, the F-test, and interpretation of results in biological contexts.
By the end of the course, students will be able to apply these statistical tools to analyze real biological data, interpret results critically, and communicate findings effectively.
- Créateur de cours: Hanane Ben Gherbal
This course provides a comprehensive overview of three major fields of microbiology:
- Mycology: study of fungi
- Algology: study of algea
- Virology: study of viruses
- focusing on their biology, ecology and significance in the environment, health and biotechnology.
- Créateur de cours: Sara Redouanesalah
Molecular Biology and Genetic Engineering
Molecular biology and genetic engineering are interdisciplinary fields that study the molecular mechanisms of life and apply this knowledge to manipulate genetic material. Molecular biology focuses on understanding the structure and function of DNA, RNA, and proteins, as well as their interactions in cellular processes. Genetic engineering uses this knowledge and laboratory techniques to directly modify genetic material, enabling applications in medicine, agriculture, industry, and fundamental research.
- Créateur de cours: samia charifi