Formation des enseignants nouvellement recrutés
The Structure 2 course places fundamental emphasis on structure as part of architectural form in the same way as function, and enables students to acquire the basic knowledge and skills needed to design a structure as the genesis of an architectural project.
- Dr.: abdelaziz brouthen
- Dr.: imadeddine debbabi
- Dr.: ABDELKADER DRAM
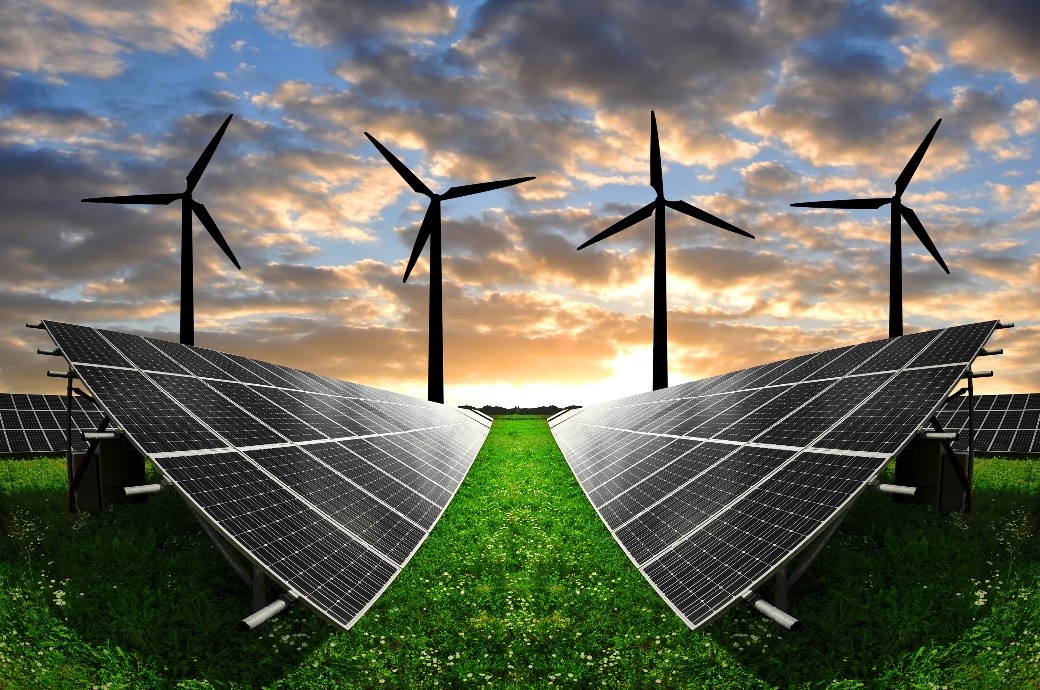

résumé du cour:
Cette cours propose aux étudiants énergies renouvelables en électrotechnique une formation sur les applications et dimensionnement des systèmes à énergies renouvelables. Un bon dimensionnement d'un système à énergie renouvelable intégré au réseau électrique peut améliorer l'efficacité et le service du réseau.
public cible:
ce cours destiné aux étudiants de la formation du master II spécialité Energies renouvelables en électrotechnique.
objectifs:
-Susciter l'intérêt de l'étudiant aux énergies renouvelables en général et aux systèmes énergétiques exploitant l'énergie solaire en particulier.
-Faire acquérir à l'étudiant une certaine compétence dans le dimensionnement d'une installation photovoltaïque.
-Mise en théorique et pratique le dimensionnement de pompage solaire.
- Dr.: nassima Bekhoucha

This course explores the concept of limits and boundaries in habitat anthropology. Spaces are not only defined by their physical characteristics but also by their social and cultural dimensions. Understanding the limits between these spaces is crucial to comprehending the ways in which people inhabit and interact with their environment. A
nthropologists and architects alike have shown a keen interest in studying the notion of limits in habitat anthropology. Amos Rapoport's work on the "built environment" is particularly noteworthy, as he argues that the design of spaces is influenced by a range of factors, including social norms, cultural beliefs, and individual preferences.
Through exploring the division of humanized and non-humanized spaces, the separation of upper and lower spaces, and the thresholds and crossings that take us from one space to another, this chapter seeks to gain a deeper understanding of how people interact with their environment and how this interaction shapes the spaces they inhabit.
Ultimately, this exploration sheds light on the implications of space thresholds for our built environment.
Learning objectives
At the conclusion of this course, you will have achieved the following goals in terms of knowledge, skills, and attitudes:
1. Knowledge Goals:
- Develop a comprehensive understanding of the concept of physical, visual, and symbolic limits.
- Analyze and articulate the key characteristics that distinguish humanized and nonhumanized spaces.
- Gain insights into the importance of designing effective transition spaces and their role in creating functional environments.
- Acquire knowledge of the application of vertically and horizontally defined limits to a given space.
2. Skills Goals:
- Demonstrate the ability to analyze and evaluate the characteristics of spaces based on their humanized and non-humanized nature.
- Apply critical thinking to assess the effectiveness of transition spaces and propose design improvements.
- Utilize the concept of vertical and horizontal limits to inform the design and layout of spaces.
- Demonstrate proficiency in articulating and communicating ideas related to the concept of limits in habitat anthropology.
3. Attitude Goals:
- Cultivate an appreciation for the complexities of limits and boundaries in shaping human experiences within the built environment.
- Develop a sense of sensitivity and empathy towards the needs and interactions of individuals with their surroundings.
- Foster a proactive and creative mindset when considering the design and optimization of spaces.
- Embrace a commitment to continuous learning and exploration in the field of habitat anthropology.
- Enseignant: Safieddine OUNIS
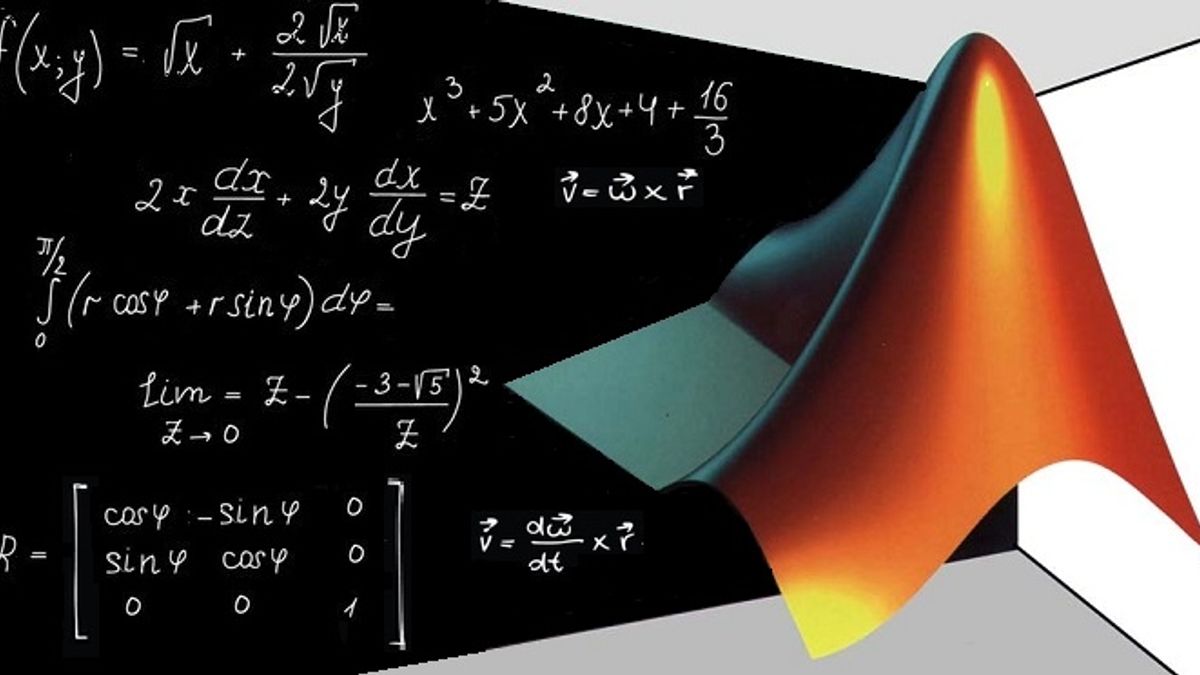
Why teaching this course ?
The benefit of this course is to teach the student how to program using easily accessible MATLAB software
version 2010.
This subject will be a tool for the realization of the practical work of the Numerical Methods in 2nd semester.
The advantage of using MATLAB over many other programming languages is that MATLAB contains
functions that enable the user and/or the student to solve various mathematical problems, such as
- Interpolation,
- Roots of algebraic equations,
- The relative minimum and maximum of a function,
- A system of linear algebraic equations,
- Curve-fitting problems,
- Definite integrals,
- A system of ordinary differential equations,
- And many others.
- Enseignant: MAHDI ABDEDDAIM
- Enseignant: Nourelislam Boumekik
- Enseignant: Salah Djerouni
a qui est destiné le cours et brève description
- Dr.: Houria Athmani
